Water-Saving Irrigation Technologies

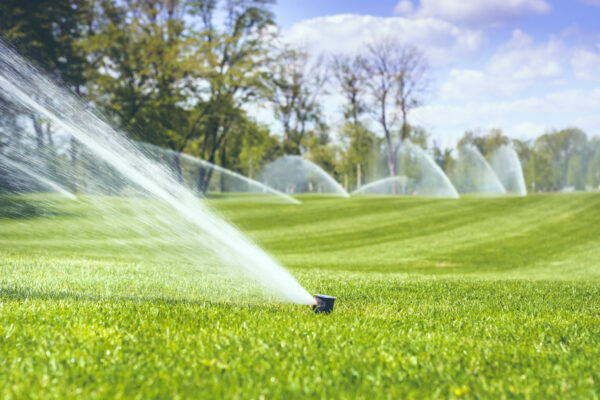
Sprinkler Irrigation
The water consumption of sprinkler irrigation is 30% lower than that of flood irrigation. The primary use is for densely planted crops in the field and is suitable for regional control. The advantage of this method is to increase yield and improve the utilization rate of cultivated land, but it also has high energy consumption and large evaporation losses, making it a requirement of large-capacity water sources. Only conditions with no more than 3 winds can be used for this method.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is an advanced irrigation technology that saves water. By using this technology, water can only be provided to the water-required parts of crops, transforming from ‘watering the land’ to ‘watering the crops’. In facility agriculture and commercial crops, drip irrigation is utilized, and it can be used in all terrains and soils, with water-saving and yield-increasing effects, and is uniform irrigation. Compared to sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation can save at least 50% of water. Water and fertilizer can easily be integrated through drip irrigation. Nonetheless, drip irrigation requires a higher level of water quality and daily system maintenance.
Underground Drip Irrigation
In recent years, underground drip irrigation has become the most advanced irrigation technology. Underground drip irrigation for fruit trees and lawns was researched and experimented on by the United States and Australia in 1998. The experiment of underground drip irrigation in cotton fields in Shihezi, Xinjiang was initiated by Israel in June 2004. In China, underground drip irrigation has been successfully implemented in Beijing, Tianjin, Jiangsu, and Xinjiang since 1996 for fast-growing forests, fruit trees, lawns, and urban greening plants. Underground drip irrigation has very little evaporation, which is completely windless and allows for precise three-dimensional placement of water and fertilizer irrigation. The use rate of water is as high as 0.98, and theoretically, there is a minimal loss of water. The loss of facilities is small, not influenced by ultraviolet radiation, and not easily deteriorated.
You may also like